...
In essence, Service Providers need to decide whether a Service Consumer is allowed access to a certain resource. To take the right access decisions, Service Providers need to interpret all relevant evidence to come to a decision: in other words: a 'logical sum' of evidence. This page further elaborates on situations where more than one delegation are issued that have overlapping properties.
...
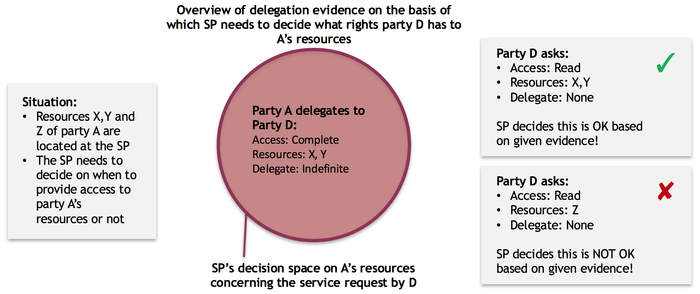
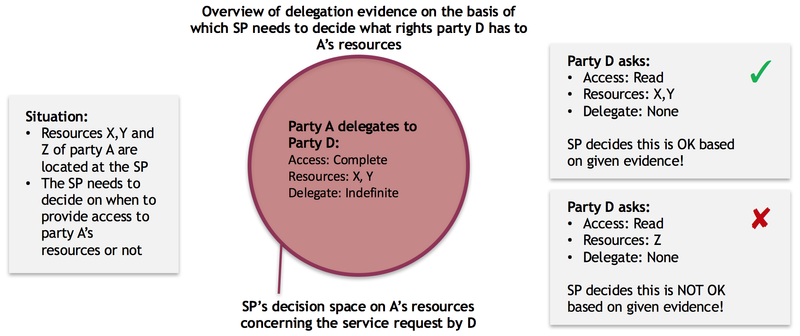
In the situation of a single delegation, a Service Provider could encounter the following situation:
Example 2: Simple path of delegation
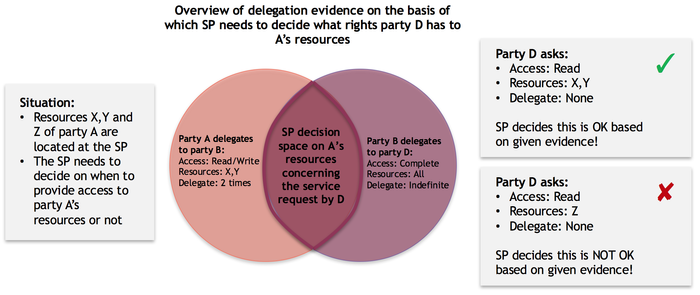
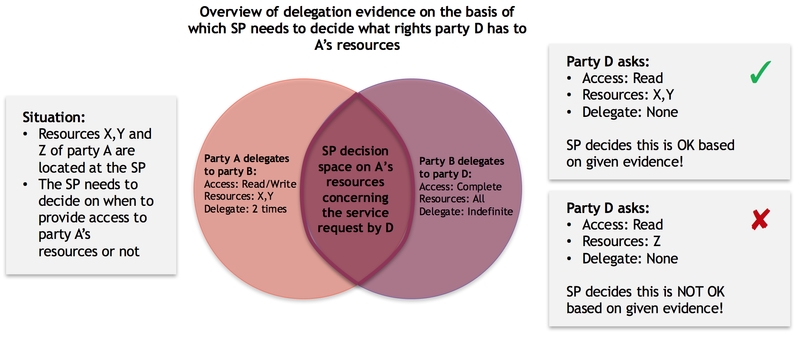
In practice, it can occur that various organisation delegate rights to various other organisation. Combining these delegations, a 'path of delegation' can be established, as is illustrated in the following example:
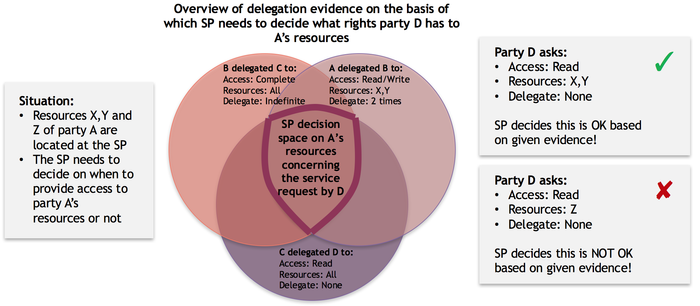
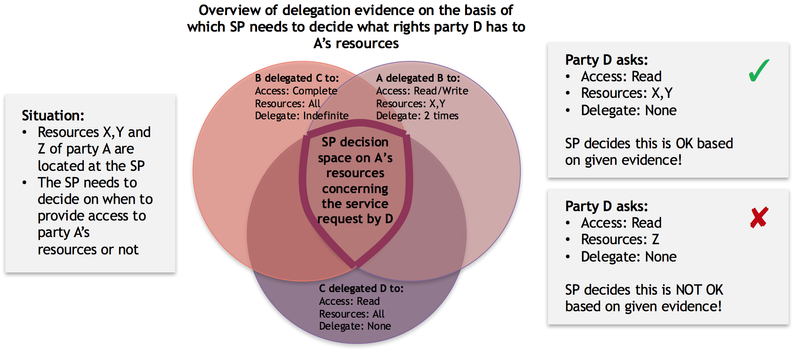
Example 3: Complex path of delegation
The following example illustrates a more complex delegation situation, where specific rights are delegated in terms of actions, resources and the right to further delegate these rights:
Party Q resides over party A's resources. When evaluating the available delegation evidence, organisation Q can conclude that organisation D has 'read' rights to resources X and Y but is not allowed to delegate these reading rights any further.
...